The battery assembly process brings together electrodes, separators, and electrolytes. And it requires different manufacturing orders and techniques by the battery shape. Let’s start with how the pouch-type battery is assembled!
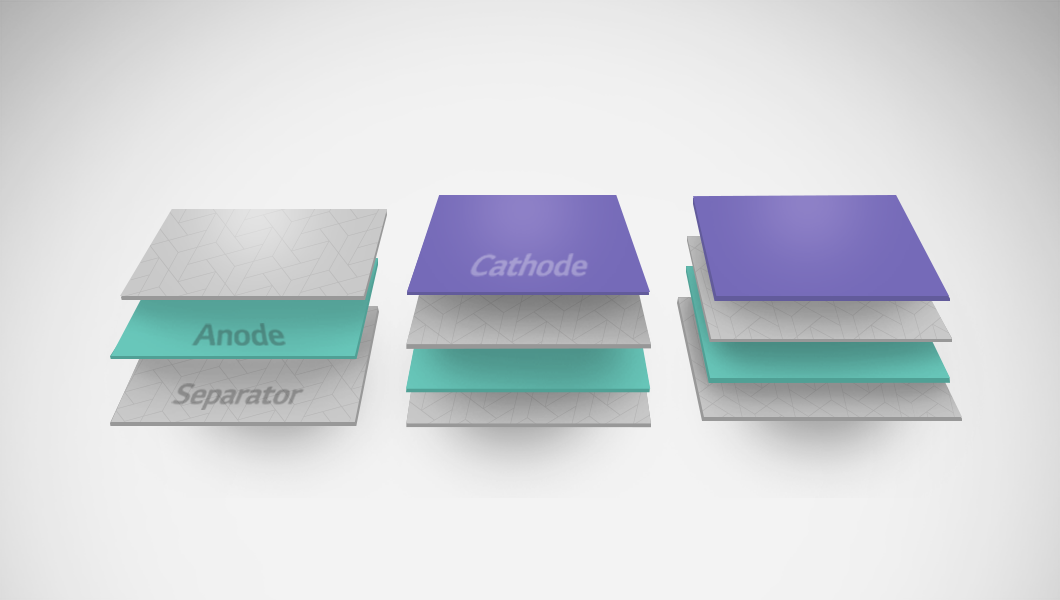
Technology for Layering Battery Materials
To insert battery materials into the electrode pockets of a pouch case, a mono-cell is first required. A mono-cell is the basic unit cell of a battery, consisting of an electrode and two separators, arranged in a stacked structure like separator-central electrode-separator-outer electrode.
The lamination & stacking method is applied to this mono-cell. First, the cathode, anode, and separators are laminated, followed by the repeated layering of mono-cells through stacking. When half-cells, composed of an anode and two separators, are stacked, a cell stack is formed, where the cathode and anode are alternately layered with separators in between.
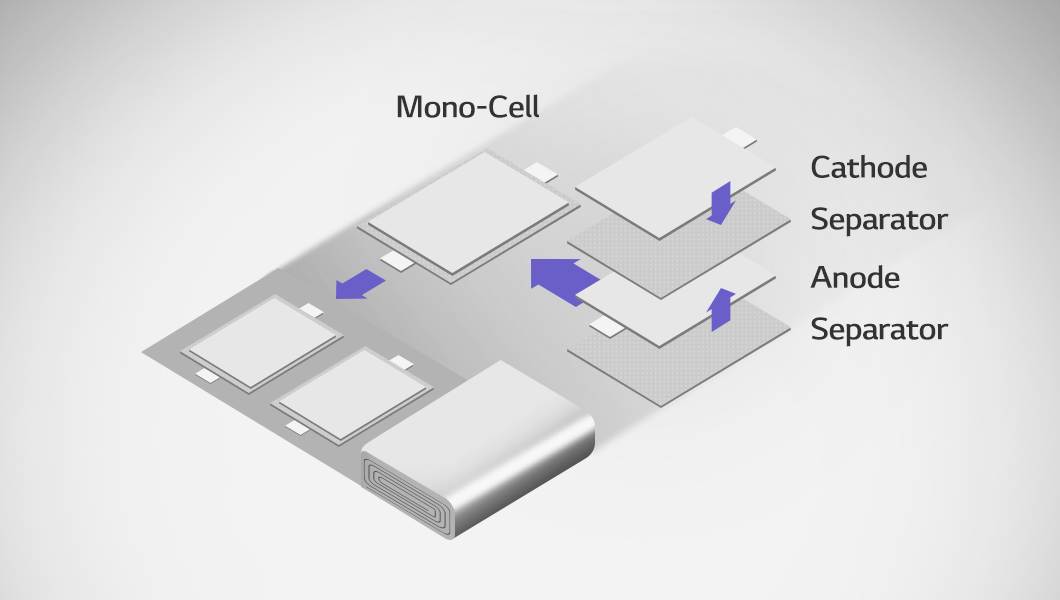
Technology for Maximizing Space Efficiency and Enhancing Energy Density
The lamination & stacking method is a technology that maximizes space efficiency inside the pouch case, thereby increasing energy density. The stacking method, which involves layering battery cells one by one, requires a high level of technical expertise. By utilizing lamination & stacking, cell misalignment is minimized, and there are no empty spaces within the battery cell, resulting in improved energy performance. Thanks to this method, LG Energy Solution produces a wide range of pouch-type batteries, from ultra-slim batteries less than 2mm thick to long cells.
We’ve explored the lamination & stacking method in the assembly of pouch-type batteries. Next time, we’ll delve into how the packaging process is carried out!





