The rechargeable batteries can be categorized into various types based on their materials. Currently, lithium-ion batteries are the most widely used batteries. Since it was first commercialized in 1991, lithium-ion batteries have been servicing various fields even today in 2022. However, as the battery need for electric vehicles and ESS, the world is looking for next-generation batteries.
One of the future batteries garnering attention is the lithium-sulfur battery.

Lithium-sulfur batteries use sulfur as cathode and lithium metal as anode. Sulfur used as cathode for lithium-sulfur batteries is less expensive than cobalt used in lithium-ion batteries. Since the sulfur cathode and lithium anode have low density and high capacity per weight than lithium-ion batteries, the battery’s energy density can become two-fold (>500Wh/kg). In other words, the lithium-sulfur battery is rising as a next-generation battery since it could offer high capacity at a lower price.
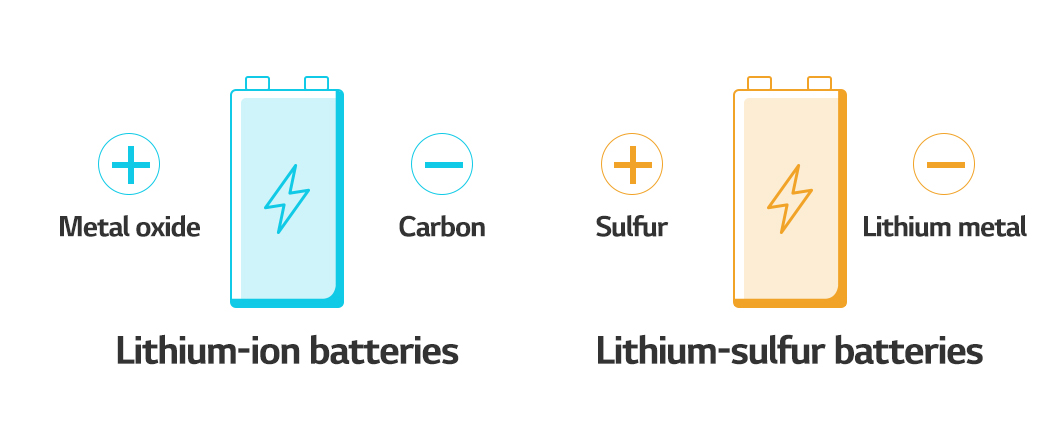
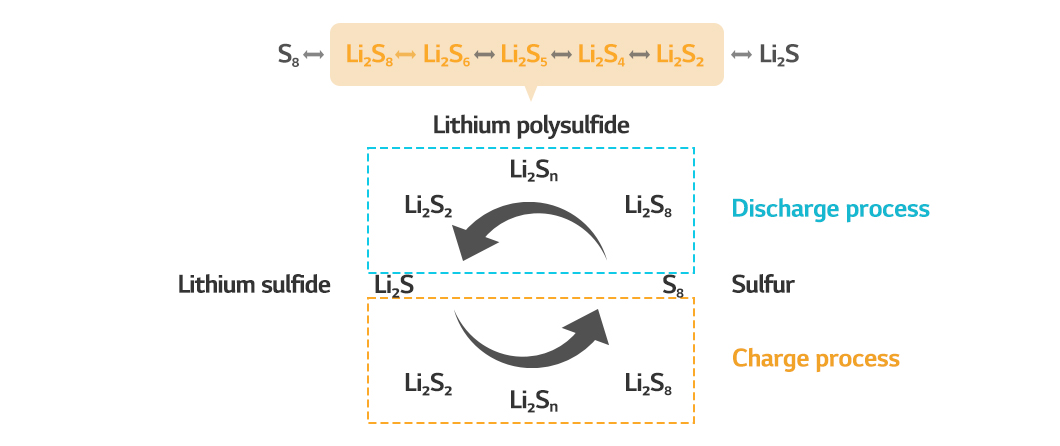
Lithium-ion batteries charge and discharge as lithium ions travel between the cathode and anode, whereas lithium-sulfur batteries generate electrical energy through the ‘gradual transition of sulfur.’ In lithium-sulfur batteries, eight sulfur atoms form a ring and consecutively trigger a reduction reaction. The ring gradually shortens and becomes a linear structure of lithium sulfide, releasing energy. Since it can be reduced until one sulfur atom bonds with two lithium ions, a large amount of lithium can be oxidized. During charging, the oxidation reaction occurs in the reverse order, converting lithium sulfide to sulfur.
Lithium-sulfur batteries have many benefits, including competitive price since it uses widely available and inexpensive sulfur. It also has a high weight reduction potential due to having twice more energy density per weight than lithium-ion batteries. Also, since it does not use rare metals like cobalt or nickel, it is environment-friendly and can be used in future mobility machines such as drones or planes. In fact, in 2020, LG Energy Solution installed a lithium-sulfur battery in a High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Solar-powered Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) developed by the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI). It successfully performed well in a test flight at the highest altitude possible in the stratosphere for 13 hours.
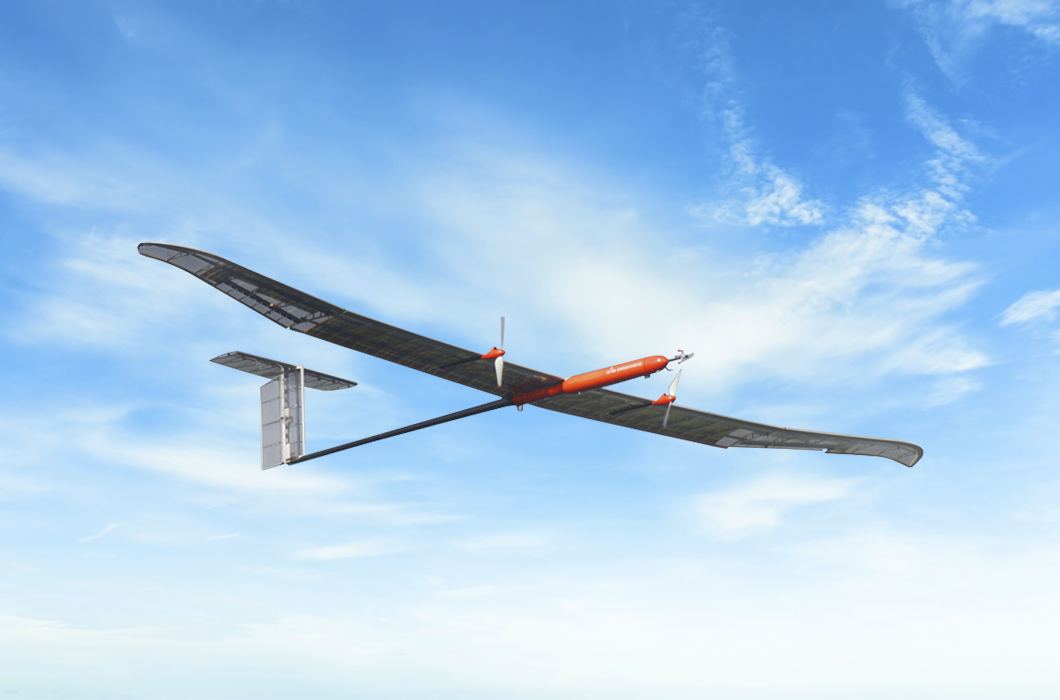

This confirms that the battery exhibits stable performance even in extreme environments at a temperature of -70 degrees Celsius and with very low atmospheric pressure that is only 1/25 of the ground level.
The lithium-sulfur battery has already been patented by American scientists Herbert Danuta and Ulam Juliusz in 1962. Its commercial application, however, did not bear fruit due to some technical problems until now. Last April, during Battery Day 2021, LG Energy Solution announced its plans to commercialize lithium-sulfur batteries beginning 2025, capturing the attention of many people.
When used commercially, lithium-sulfur batteries are expected to power the URM (Urban Air Mobility). It may not be far out in the future when LG Energy Solution serves the drone industry with its lithium-sulfur battery technology. The images we usually see in sci-fi movies involving flying cars or air taxis in busy cities may become a reality sooner than we think. How great would it be when the day comes!





