As demand for batteries increases across diverse industries such as automotive, energy, and IT, ensuring transparency throughout the entire lifecycle—from production and use to disposal—has become essential. Amid this trend, the concept of the battery passport has drawn significant attention. Let’s look into what it is and the information it contains.

Battery Passport Background and Concept
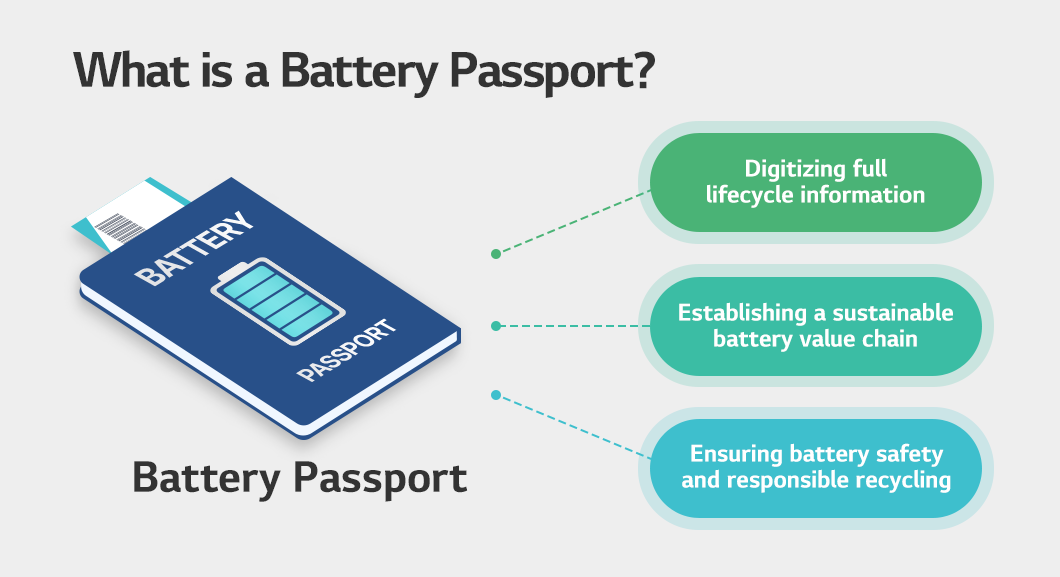
The battery passport is a regulatory requirement that will become mandatory in the EU starting in 2027 to ensure battery safety and responsible recycling. Each battery is assigned a unique digital ID that provides information about its entire lifecycle, including production, use, disposal, reuse, and recycling. Simply put, it serves as a digital passport that shows a battery’s journey.
First proposed by the Global Battery Alliance (GBA)1 at the World Economic Forum in 2020, the battery passport was conceived to facilitate resource circulation and strengthen the value chain. Acknowledging the significance of GBA’s initiative, the EU incorporated the battery passport into its new battery regulation to advance a circular economy. Under this regulation, a battery passport is required for all batteries with storage capacities greater than 2 kWh sold in the EU market.
Components of a Battery Passport
Through the battery passport, anyone can access key information by scanning the QR code affixed to the battery. So, what details are included?
First, it provides manufacturing information including the manufacturer’s name, battery classification, identification number, production date, and the location of the manufacturing facility. It must also specify the battery’s weight, capacity, chemical properties, and the appropriate fire-extinguishing agents. In addition, the passport contains information on raw materials, including the origin of lithium and cobalt, supply chain details, and the presence of hazardous substances. Finally, it presents sustainability information such as carbon footprint, the proportion of recycled materials used, repurposing history, recycling records, and ESG scores.
With these features, the battery passport is expected to deliver practical value to a wide range of stakeholders as a tool for tracking and managing the entire lifecycle of a battery. For consumers, it can support more responsible choices based on the data recorded in the battery passport by allowing them to consider the environmental and social impacts of their purchases. For companies and institutions, it helps them clearly identify supply chain activities and environmental impacts and use these insights to develop strategies for carbon footprint reduction and recycling.
LG Energy Solution, Leading the Introduction of the Battery Passport
LG Energy Solution joined the GBA in 2022, becoming the first global battery maker to participate in the battery e-passport development project. Recently, the company unveiled its battery passport system pilot at InterBattery Europe 2025 and announced plans to develop and operate its own Battery Regulation Management (BRM) system.

We have reviewed the battery passport, which has emerged as a key initiative in the battery industry. With the EU’s 2027 battery passport mandate approaching, LG Energy Solution will take preemptive steps to establish a sustainable battery ecosystem built on the battery passport system.
- Global Battery Alliance (GBA): A public-private collaboration platform founded at the World Economic Forum in 2017 to establish a sustainable battery value chain by 2030 ↩︎