Batteries are categorized into cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch form factors, each with distinct manufacturing processes and characteristics. Among these, the pouch type minimizes unused space inside the cell and achieves high energy density through a stacking method. Its thin, flat structure maximizes volumetric energy efficiency in module and pack design, while also allowing production in diverse shapes and sizes for versatile applications.
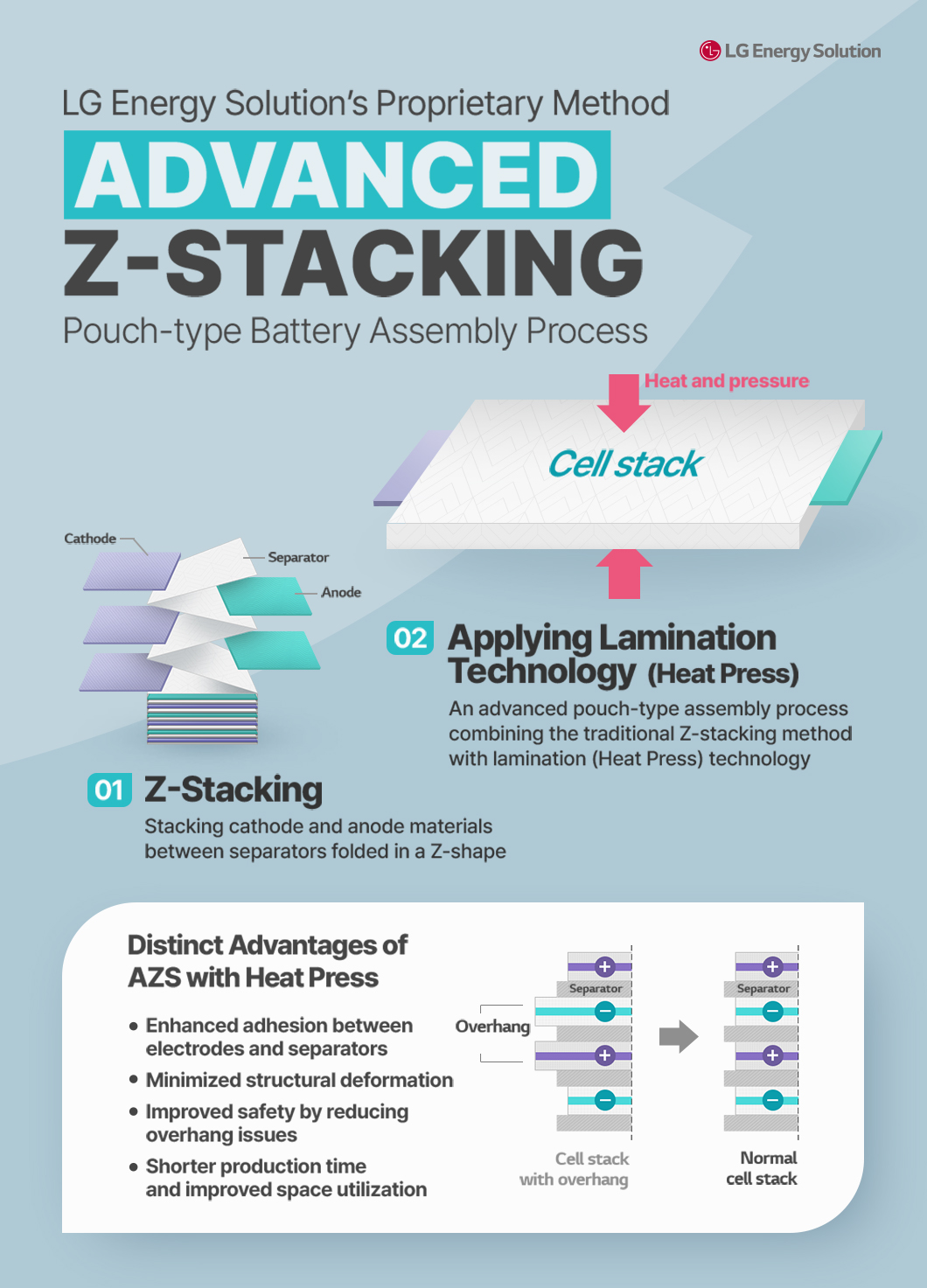
LG Energy Solution continues to drive innovation in pouch battery manufacturing technology. Recently, the company introduced Advanced Z-Stacking (AZS), a new method that combines Lamination & Stacking (L&S) with Z-Stacking. The infographic below illustrates LG Energy Solution’s latest AZS process.
LG Energy Solution, a Pioneer in Pouch-type Batteries
LG Energy Solution has made significant efforts in the research and development of pouch-type batteries. The technological capabilities it has accumulated since beginning mass production in 2000 now provide the foundation for its leadership in the pouch-type battery market.
One of the secrets to its market leadership is its proprietary Lamination & Stacking technology.
L&S involves lamination, which aligns and bonds the cathode, anode, and separator, followed by stacking, which repeatedly layers the laminated monocells into half-cells. By maximizing the use of space inside the battery cell, this method increases energy density while also improving productivity.
AZS, LG Energy Solution’s Innovative Pouch Battery Manufacturing Method
LG Energy Solution has once again pioneered innovation in the pouch battery market with the development of a new manufacturing process, AZS.
In Z-Stacking, the cathode and anode are alternately piled between Z-folded separators. LG Energy Solution combined the advantages of its proprietary Lamination & Stacking with Z-Stacking, thereby enhancing battery safety.
In the AZS process, the cathode, anode, and separator are first layered through Z-Stacking, after which lamination is applied. What distinguishes AZS from conventional Z-Stacking is the addition of a heat-press step that applies heat and pressure to strengthen adhesion between electrodes and separators.
The application of the heat-press step provides much higher safety than Z-Stacking, as it minimizes structural deformation by firmly bonding electrodes and separators with heat and pressure. In particular, it markedly improves safety by fundamentally addressing the overhang issue, where parts of the electrodes protrude from the stacked layers of cathodes and anodes. In addition, AZS shortens manufacturing time because the stacked cells are already bonded during the process, enabling easier handling and the transfer of more cells during process-to-process transfer.
LG Energy Solution has adopted AZS in its manufacturing lines, advancing the production of pouch-type batteries with this method. Currently, AZS-based mass production is underway at PT. HLI Green Power in Indonesia.
Through this infographic, we looked into LG Energy Solution’s innovative AZS technology and learned how it differs from conventional Z-Stacking. We will continue to share various battery technologies in easy and fun ways through our infographics!