In electric vehicle (EV) batteries, a set of cells is assembled into a module, and multiple modules are assembled to form a pack. Each cell must maintain a consistent voltage to ensure battery performance and lifespan. If a voltage difference occurs, the cell balancing function activates to correct it. This time, we will take a closer look at what cell balancing is and how it works.
*View Battery Glossary – Cell Balancing
What is Cell Balancing?
Cell balancing is the process of adjusting voltage differences between the cells that make up a battery to equalize them. This is performed by the battery management system (BMS) installed in the pack. The BMS not only controls charging and discharging voltage, current, and temperature to ensure battery safety, but also optimizes efficiency through cell balancing.
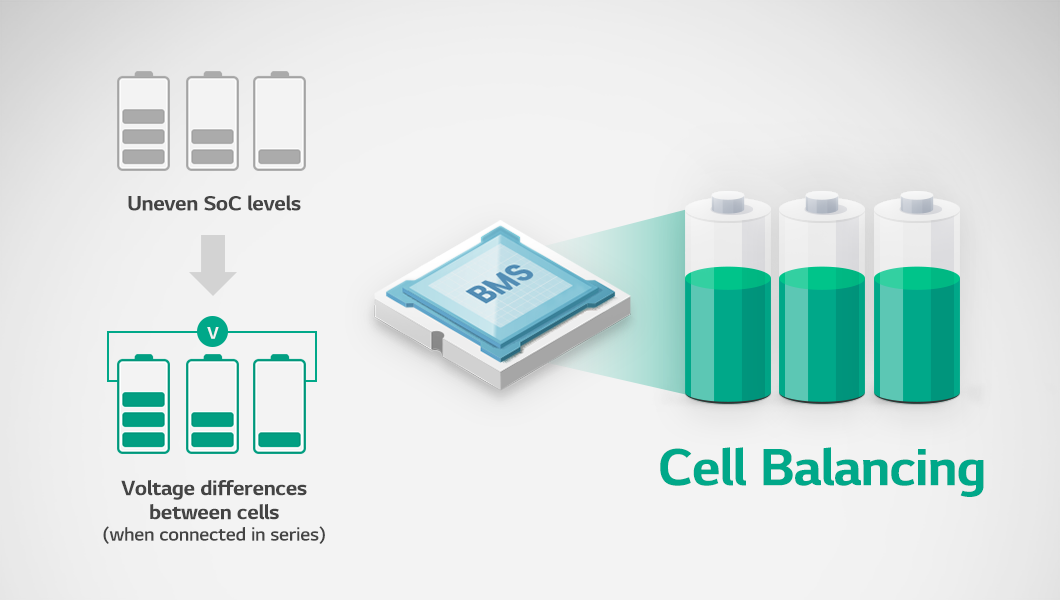
Lithium-ion batteries maintain a state of charge (SoC) range of 20% to 80% to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, but discrepancies among cells can occur due to various factors.
When a battery is charged and discharged under conditions where voltage differences between cells exist, overcharging and over-discharging may occur in certain cells, leading to voltage discrepancies among the cells. Therefore, the cell balancing function is essential for maintaining battery efficiently and ensuring stable management.
Methods of Cell Balancing: Passive and Active Cell Balancing
Cell balancing can be broadly classified into two methods: Passive Cell Balancing and Active Cell Balancing.
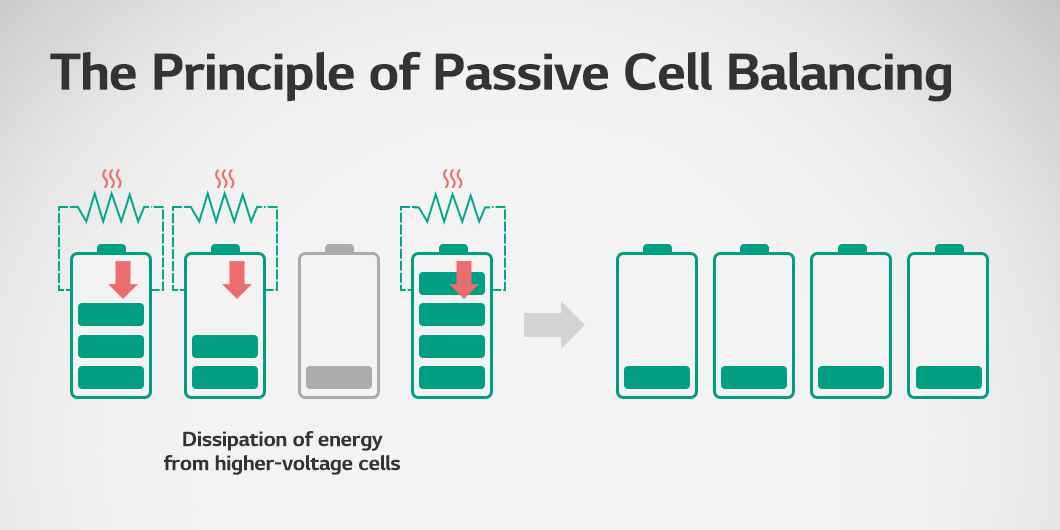
Passive cell balancing is a method that can be applied during battery charging. It uses resistance to dissipate excess energy from high-voltage cells as heat, balancing their voltage with the other cells. This method is easy to implement, cost-effective, and requires minimal system space, making it an economical option. However, in passive cell balancing, energy is dissipated solely as heat and cannot be reused. As a result, energy efficiency is low.
Passive cell balancing can be further divided into the Fixed Shunting Resistor method and the Switched Shunting Resistor method. The Fixed Shunting Resistor maintains cell voltage at a constant level using a fixed resistor, and its simple circuit design makes it cost-effective. The Switched Shunting Resistor method controls resistance using switches, assigning a resistor and switch to each cell to adjust voltage.
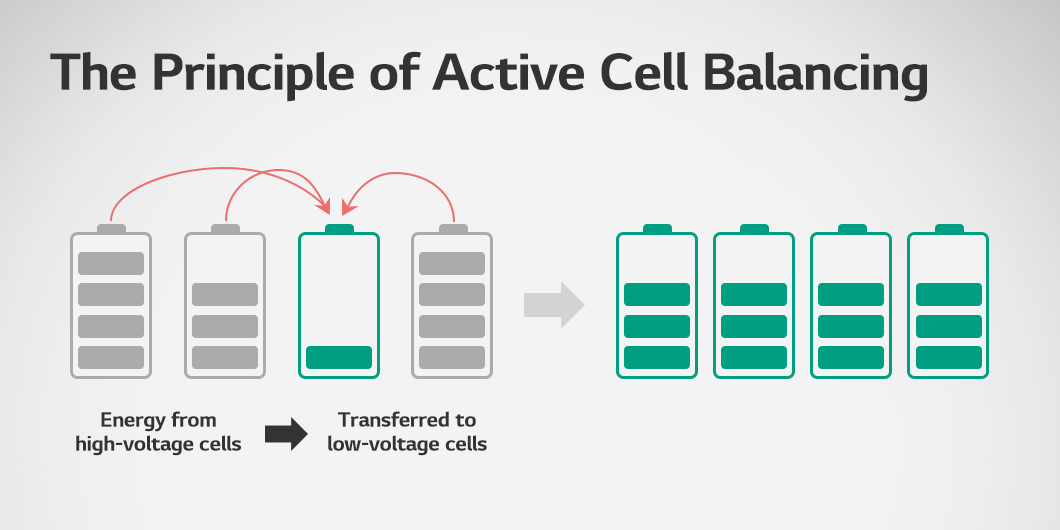
Active cell balancing works by transferring energy from high-voltage cells to low-voltage cells. This approach distributes energy to enhance energy efficiency and can be applied during both charging and discharging. However, it requires a complex system structure and advanced technical capability, resulting in relatively higher costs to configure a circuit. Active cell balancing can be classified based on the energy transfer mechanism between cells, such as the use of capacitors, converters, or transformers.
Let’s compare the principles of passive cell balancing and active cell balancing using Figures 1, 2, and 3.
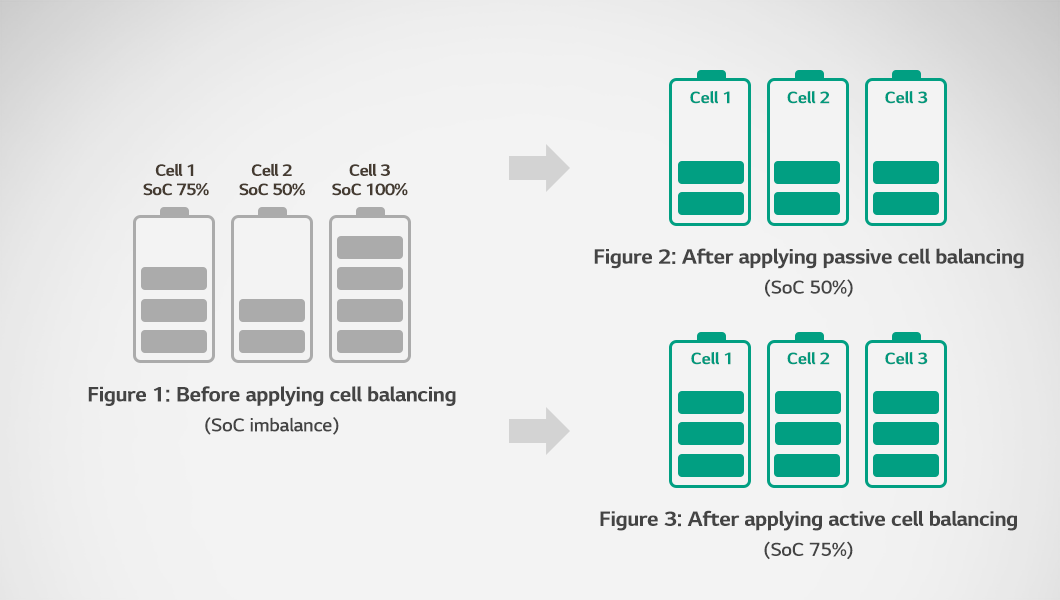
Figure 1 shows a condition where cell balancing is not applied. In this state, energy imbalances can occur among Cell 1, Cell 2, and Cell 3 due to differences in their SoC levels. Figure 2 illustrates the application of passive cell balancing. Using Cell 2, which has the lowest SoC and voltage, as a reference, excess energy from Cell 1 and Cell 3 is dissipated to match Cell 2. Active cell balancing is depicted in Figure 3. This method redistributes energy from the cells with higher SoC and voltage to those with lower levels, achieving balance across all cells with minimal energy loss.
The Core Function of Batteries: The Future of Cell Balancing Technology
As the demand for high-capacity batteries increases, the number of cells in a battery pack grows correspondingly. In particular, EVs and energy storage systems (ESSs) require hundreds to thousands of cells. Therefore, sophisticated cell balancing technology is necessary to make full use of the battery’s performance.
In line with this trend, various studies on cell balancing are being conducted within the battery industry. One of them, hybrid cell balancing technology that combines passive and active cell balancing methods, is gaining attention. It activates passive cell balancing when the imbalance between cells is minor, and performs active cell balancing when the imbalance is significant. This approach efficiently transfers energy between cells while maintaining a simple structure, and can reduce costs. Additionally, with the continuous advancement of artificial intelligence (AI), intelligent cell balancing utilizing AI is being explored.
Cell balancing is an important technology that reduces voltage differences between battery cells and equalizes their SoC. This technology enables us to use batteries more efficiently and safely. Ensuring battery efficiency and safety, cell balancing will continue to evolve – stay tuned to see how it advances in the future.